Complete a Review About the Main Genetic Disorder
-
Hereditary genetic disorders are passed downwards from generation to generation.
-
Spontaneous genetic disorders are not passed downward from one generation to another, but they occur when genetic material in the male parent'southward sperm or mother's egg cells or in the cells of the developing embryo is damaged by take a chance or by drugs, chemicals, or other damaging substances (such as x-rays).
-
Before women get pregnant, they and their partner should speak with their health intendance practitioner almost their risk of having a baby with a genetic disorder.
-
Hazard factors include older age in the woman, a family history of genetic abnormalities, a previous baby with a birth defect or miscarriage, and a chromosomal abnormality in one of the prospective parents.
-
Testing for genetic disorders is offered to all women but is particularly important if a couple'south risk is higher than normal.
Couples who are thinking of having a baby should speak with their health care practitioner virtually the risks of genetic abnormalities (prenatal genetic counseling). They can discuss precautions that they can take to help prevent some genetic abnormalities. For example, women can avoid exposure to toxic substances and radiation.
-
Artificial insemination if the man has an abnormal gene
-
Utilise of an egg from some other woman if the woman has an aberrant factor
Couples should take time to absorb the information and should enquire any questions they accept.
All pregnancies involve some risk of genetic abnormalities.
The following percentage of all babies have an aberration:
-
0.five% accept a chromosomal disorder.
-
ane% have a single-gene (mendelian) disorder.
-
1% accept a disorder caused by defects in several genes.
The percentage of stillborn babies with an aberration is fifty-fifty higher.
Yet, certain weather condition increase risk.
Some birth defects, such as cleft lip or palate Crack Lip and Cleft Palate The well-nigh common birth defects of the skull and face up are cleft lip and crack palate, affecting about 2 of every ane,000 babies. Cleft lip is a separation of the upper lip, usually simply beneath the... read more 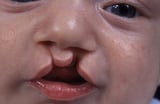 , event from abnormalities in i or more genes plus exposure to sure other factors, including substances in the environment (called multifactorial inheritance). That is, the abnormal factor makes the fetus more likely to develop a birth defect, but the birth defect usually does not develop unless the fetus is exposed to specific substances, such every bit certain drugs or alcohol Overview of Substance-Related Disorders Drugs are an integral part of everyday life for many people, whether the drugs are used for legitimate medical purposes or recreationally (run across table Drugs with Medical and Recreational Uses)... read more . Many mutual nascence defects, such every bit heart malformations, are inherited in this mode.
, event from abnormalities in i or more genes plus exposure to sure other factors, including substances in the environment (called multifactorial inheritance). That is, the abnormal factor makes the fetus more likely to develop a birth defect, but the birth defect usually does not develop unless the fetus is exposed to specific substances, such every bit certain drugs or alcohol Overview of Substance-Related Disorders Drugs are an integral part of everyday life for many people, whether the drugs are used for legitimate medical purposes or recreationally (run across table Drugs with Medical and Recreational Uses)... read more . Many mutual nascence defects, such every bit heart malformations, are inherited in this mode.
-
Family unit history: The chance of having a babe with a neural tube defect is increased by having a family member, including the couple'due south children, with such a defect (family unit history). For couples who accept had a babe with spina bifida or anencephaly, the take chances of having another baby with one of these defects is ii to 3%. For couples who have had ii children with one of these defects, the adventure is 5 to x%. However, about 95% of neural tube defects occur in families without a history of neural tube defects.
-
Geographic location: Risk also varies based on where a person lives. For example, adventure is higher in the United Kingdom than in the United States.
A few neural tube defects effect from hereditary abnormalities in a single gene, from chromosomal abnormalities, or from exposure to drugs.
Several factors increment the run a risk of having a babe with a chromosomal aberration:
-
Woman's age: The risk of having a babe with Down syndrome increases with a woman's age—steeply after historic period 35.
-
Family unit history: Having a family history (including the couple's children) of a chromosomal aberration increases the risk. If a couple has had ane baby with the most common class of Down syndrome (trisomy 21) and the adult female is younger than 30, the risk of having another baby with a chromosomal abnormality is increased to about one%.
-
Chromosomal abnormality in a prospective parent: Rarely, a prospective parent has a structural chromosomal aberration that increases the risk of having a babe with a structural chromosomal abnormality. A chromosomal abnormality in one or both parents increases the risk, even if the afflicted parent is salubrious and has no concrete sign of the abnormality. Doctors suspect such an abnormality when couples have had several miscarriages, bug with infertility, or a babe with a nascency defect. For such couples, the risk of having a baby with a serious chromosomal aberration is increased, equally is the adventure of miscarrying.
Some chromosomal abnormalities cannot be detected past standard chromosomal testing. Near of these abnormalities are too small to be seen with a microscope, so they are sometimes called submicroscopic abnormalities (or re-create-number variants). For example, a very small function of a chromosome may be missing (chosen a microdeletion), or a chromosome may have a very small extra part (chosen a microduplication). How oft microdeletions and microduplications occur is unknown. However, virtually half dozen% of children with structural nascence defects take them, fifty-fifty though results of standard chromosomal testing are normal. Tests called chromosomal microarray testing can detect microdeletions and microduplications. Doctors may offer microarray testing earlier nascency in sure circumstances—for case, when nativity defects are suspected in a fetus.
However, girls must inherit two abnormal genes to develop an Ten-linked disorder if the gene is recessive. If the abnormal gene is dominant, only one abnormal factor is required for the disorder to develop.
If the prospective mother and male parent are related, they are more than likely to have the same mutation in i or more of the genes that crusade autosomal recessive disorders. Thus, the risk of such disorders is increased.
The following is an English-language resources that may exist useful. Please note that THE Transmission is not responsible for the content of this resource.
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/detection-of-genetic-disorders/overview-of-genetic-disorders
0 Response to "Complete a Review About the Main Genetic Disorder"
Post a Comment